What Is a Coreless DC Motor and How Does It Work
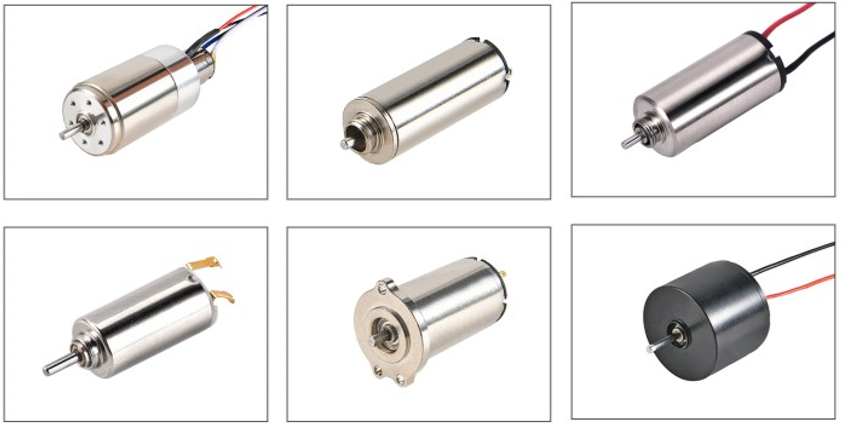

A coreless dc motor has a rotor with no iron core. The copper windings are shaped like a basket. This makes the motor lighter and faster. It spins more easily than other motors. Coreless dc motors move smoothly and very precisely. They do not make much vibration or noise. These motors work better and do not get as hot. Your devices can stay cooler and quieter.
Coreless dc motors are very precise and respond quickly. They are great for jobs that need speed and accuracy.
Key Takeaways
Coreless DC motors do not have an iron core in the rotor. This makes them lighter and faster than regular motors. These motors run smoothly and quietly. They make less heat, so devices stay cool and last longer. Coreless motors react quickly and give precise control. They are great for small, accurate, and quiet uses. They use less energy and cause less wear. This means less fixing and a longer motor life. Coreless motors are not good for heavy jobs. They make less torque and can get too hot if used too much.
What Is a Coreless DC Motor
Definition
A coreless dc motor is a kind of electric motor. It does not have an iron core inside the rotor. The copper windings are shaped like a basket and are hollow. This makes the motor much lighter than regular motors. Because the rotor is light, it can start and stop very fast. The motor also stays cooler and uses energy better. There is no iron to make extra heat or waste energy.
Coreless dc motors are used in devices that need quick and exact movement. They use rare earth magnets in the stator. These magnets help make strong magnetic fields even without an iron core. Epoxy holds the windings together, so the rotor is strong and lasts long. This special design lets the motor run smoothly and quietly. That is important for equipment that needs gentle movement.
Key Differences
When you look at a coreless motor and a regular DC motor, you see some big differences. Here are some main points:
The rotor in a coreless dc motor does not have an iron core. Regular motors have a solid iron core.
The windings in a coreless motor make a cylinder by themselves. Regular motors wrap coils around a steel core.
Coreless motors use rare earth magnets for stronger magnetic fields.
The light rotor in a coreless motor means it speeds up and slows down faster.
You will feel less shaking and smoother movement with a coreless motor.
Coreless motors make less heat and work better because they do not lose energy in an iron core.
But, coreless motors have lower torque density, so they are not good for heavy jobs.
Tip: If you want smooth, fast, and exact movement, a coreless motor is a good pick. For tough jobs, a regular motor might be better.
Here is a table to show the main differences between a coreless dc motor and a regular DC motor:
Characteristic | Coreless DC Motor | Conventional DC Motor |
|---|---|---|
Rotor Design | Hollow cylinder/cup, no iron core | Solid iron core |
Efficiency | Higher due to elimination of iron losses | Moderate, iron losses present |
Cogging Effect | Minimal, smooth motion without cogging | Present, due to magnetic interaction |
Inertia | Low, enabling faster acceleration | High, slower response |
Heat Generation | Reduced, better heat dissipation | Higher due to iron core losses |
Torque Density | Lower, less torque per unit size | Higher torque output |
When you compare cored and coreless dc motors, you see that not having an iron core gives many good things. The motor works better, stays cooler, and moves more smoothly. It also lasts longer because there is less sparking and damage. But, remember that coreless motors are not good for heavy loads because they make less torque.
You can find coreless dc motors in many new devices. They are used where speed, accuracy, and quiet are very important.
Coreless Motor Design
Rotor Structure
Inside a coreless motor, the rotor looks different. It does not have an iron core. The rotor uses a basket-wound shape with copper wires. These wires make a hollow cylinder. This makes the rotor much lighter than in other motors. Epoxy resin or plastic holds the wires together. Without iron, the motor does not lose energy from heat. This helps the motor work better. The motor can be 75% to 90% efficient. That is better than motors with iron cores. The light rotor lets the motor speed up and slow down fast. It can start and stop in just a few milliseconds. But, the rotor is not as strong. You need to watch the heat so it does not get too hot.
No iron core in the rotor
Basket-wound copper or aluminum wires
Epoxy or plastic support
High efficiency and fast response
Stator and Magnets
The stator in a coreless motor is slotless. There are no teeth or iron sheets inside. This stops the cogging torque that causes shaking and noise. The rotor spins smoothly with no sticky spots. Strong rare-earth magnets, like neodymium, make a strong magnetic field. These magnets help the motor keep its torque, even with a bigger air gap. The slotless stator lowers inductance and makes the motor respond faster. The motor runs quietly, smoothly, and very precisely.
Slotless stator removes cogging torque
Rare-earth magnets provide strong magnetic fields
Smooth, quiet, and precise operation
Self-Supporting Windings
The windings in a coreless motor hold themselves up. They form a hollow, basket-like cylinder. Sometimes, the wires are in a slanted or honeycomb pattern. Epoxy keeps the wires together because there is no iron core. This design makes the motor lighter and lowers inertia. The motor can speed up and slow down quickly. The windings also help the motor fit in small spaces. But, without an iron core, the motor can get hot if used a lot. Many coreless motors use heat sinks or cooling ports to stay safe.
Here is a table to show how the basket-wound design compares to an iron-core motor:
Aspect | Coreless DC Motor (Basket-Wound) | Iron-Core DC Motor |
|---|---|---|
Rotor Construction | Hollow, self-supporting windings | Windings on iron core |
Rotor Mass | Much lower | Higher |
Inertia | Very low | High |
Cogging Torque | None | Present |
Structural Support | Epoxy/plastic | Iron core |
Note: The coreless motor design gives you a light and efficient motor. It moves smoothly and changes speed fast. But you need to watch for overheating if you use it a lot.
How Coreless Motors Work
Operating Principle
A coreless motor works because of its special design. The rotor does not have an iron core. Instead, it has copper windings shaped like a basket. These windings are hollow and go around strong magnets in the stator. When electricity flows through the windings, it meets the magnetic field. This makes torque, which spins the rotor. The rotor is light because there is no iron core. This helps the motor start and stop very quickly. Epoxy resin keeps the windings in place. The motor stays cool and uses energy well. It can move smoothly and with great accuracy, even at slow speeds. The motor does not shake or make much noise. This is good for devices that need to be quiet and exact.
Note: The light rotor and strong magnets help the motor move fast, smooth, and use less energy.
Commutation
Coreless motors use brushes and a commutator to work. This is like regular brushed DC motors. But the design is different. The windings make a hollow cage and are held by epoxy. There is no iron core inside. This stops iron losses and lowers winding inductance. Because of this, there is less sparking at the brushes. The brushes last longer and do not need to be changed often. You do not have to do much maintenance. The light rotor lets the motor speed up and slow down fast. The motor works better and lasts longer.
Here is a table that compares commutation in coreless and regular DC motors:
Feature | Coreless Motor | Traditional DC Motor |
|---|---|---|
Rotor Core | None (hollow windings) | Laminated iron core |
Inductance | Very low | Higher |
Sparking | Minimal | More common |
Brush Wear | Reduced | Higher |
Maintenance | Less frequent | More frequent |
Tip: If you want a motor that needs little care and lasts a long time, pick a coreless motor.
Motion Generation
Coreless motors give smooth and accurate movement because of their design and materials. Many things affect how the motor moves:
New technology makes coreless motors work better and in more ways.
The motor’s shape matters. Cylindrical motors are efficient and light, so they fit in small devices. Disc motors are flat and give more torque, which is good for robots and planes.
Better materials and building methods make the motors stronger and more efficient.
Companies want motors that are small, quiet, and powerful for their size.
Robots, electric cars, and medical tools need motors that react fast and fit in tight spaces.
Other things to think about are:
How long you run the motor changes how long it lasts.
Bearings help the motor last longer and carry loads.
You must keep the motor cool. Too much current can make it too hot and break it.
The motor’s size and weight must fit your device.
For exact movement, you might need encoders or gearboxes.
Airflow and how you mount the motor also matter.
In battery devices, you must balance power use and motor size for best results.
Remember: If you need a motor that moves exactly, smoothly, and reacts fast, a coreless motor is a great choice.
Coreless Brushless DC Motor
Brushless Design
A coreless brushless dc motor is built differently from a brushed coreless motor. It does not use brushes or a commutator. Instead, it uses electronic controllers and sensors to switch the current. This makes the motor last longer and work better. You do not have to worry about brushes wearing out. The motor is quiet and does not make much electrical noise. It is also lighter and smaller because there are no big brush parts.
Here is a table to help you see the main differences:
Aspect | Brushed Coreless DC Motors | Brushless Coreless DC Motors |
|---|---|---|
Construction | Use physical brushes and a commutator for electrical contact; brushes cause friction and wear. | Eliminate brushes and commutators; use electronic controllers and sensors (e.g., Hall sensors) for commutation. |
Mechanical Wear | Brushes and commutator wear out over time, limiting lifespan. | Minimal mechanical wear due to absence of brushes, resulting in longer service life. |
Electrical Noise | Generates electrical noise and sparking due to brush contact. | Produces less electrical noise because of solid-state commutation. |
Maintenance | Requires regular brush replacement and maintenance. | Low maintenance due to brushless design. |
Efficiency | Lower efficiency due to friction and energy loss in brushes. | Higher efficiency with reduced friction and better energy conversion. |
Size and Weight | Bulkier due to brushes and commutator components. | More compact and lighter without brushes. |
Speed and Control | Limited speed range; less precise speed and torque control. | Higher speed capability; precise speed and torque control via electronic commutation. |
Noise (Acoustic) | Noisier operation due to brush friction and sparking. | Generally quieter operation, suitable for noise-sensitive applications. |
Commutation Method | Mechanical commutation via brushes and commutator. | Electronic commutation controlled by sensors and controllers. |
Tip: If you want a motor that lasts longer and needs less care, a coreless brushless dc motor is a smart choice.
Performance Features
A coreless brushless dc motor gives you many good features. The rotor has no iron core, so it is very light. This helps the motor start and stop very fast. The motor is small and fits in tight spaces. It runs quietly because there are no brushes or iron core. You will hear less noise when it works. The motor reacts quickly and moves smoothly. This is great for robots, cameras, and medical tools. The design cuts down on both electrical and mechanical noise. Your devices work better and last longer. You can control speed and torque very well with electronics. The motor stays cool and saves energy. You do not lose power from friction or heat.
A coreless brushless dc motor is best when you need fast, exact, and quiet movement. You will find these motors in robots, medical devices, and fancy cameras. The special design helps you build smarter and more reliable machines.
Coreless Motors: Pros and Cons
Advantages
Coreless motors have many good points for your projects. They change electricity into power very well. The rotor is light because there is no iron core. This helps the motor start and stop fast. You can easily change how fast or which way it spins.
Higher efficiency: Coreless motors do not waste much energy as heat. You get more power for the same electricity.
Lower current draw: These motors use less current, so batteries last longer.
Fast response: The light rotor helps the motor speed up or slow down fast.
Smooth operation: The motor does not jerk or shake. It runs quietly and smoothly.
Less electromagnetic interference: No iron core means fewer sparks and less electrical noise.
Longer lifespan: With fewer parts wearing out, you do not need much maintenance.
Tip: If you want a motor that moves fast and smooth, coreless motors are a good pick.
Disadvantages
Coreless motors also have some things you should think about. They cost more than regular brushed DC motors. The price can be high, especially for big projects.
Limited torque: Coreless motors cannot move heavy things. They work best in small, light devices.
Higher cost: The special design and materials make these motors cost more.
Heat buildup: The small size makes the motor get hot fast, especially at high speeds or with lots of use.
Overheating risk: If you use the motor too hard for too long, the wires can get damaged. The glue that holds the wires may break down.
Not for overload: These motors do not work well if you push them too hard. You should not use them above their rated limits.
You also need to check the brushes in brushed coreless motors. Even though they last longer than iron-core types, brushes still wear out. Cleaning and following the maker’s rules help the motor last longer.
Note: Coreless motors work great for jobs that need precision, but they are not good for heavy-duty work.
Coreless Motors Applications

Coreless motors have changed how small machines work. They are light and reliable. Many industries use them because they save energy. Let’s see where coreless motors are used most.
Portable Devices
You use portable devices all the time. Coreless motors make these gadgets lighter and better. Their small size fits well in things like:
Electric toothbrushes
Handheld fans
Wireless earphones
Miniature drones
Smartwatches
These motors use less battery, so your devices last longer. They run quietly and smoothly. You can enjoy your gadgets without loud noise or shaking.
Medical Equipment
Medical devices need quiet and precise motors. Coreless motors are perfect for this. You find them in:
Infusion pumps and injection pumps
Surgical robots
Electric scalpels
Portable ventilators
Imaging equipment like MRI and CT scanners
Coreless motors do not have cogging torque. This means they run smooth and quiet. That helps keep patients safe and comfortable. The motors react fast and stay steady. This is important for careful medical work. Their light weight makes portable tools easier to use.
Tip: In robotic surgery, coreless motors help doctors move with more control. This makes surgery safer and more accurate.
Robotics
Robots use coreless motors for many jobs. The motors let robots move fast and stop quickly. This is good for robot arms, drones, and machines that work by themselves. The small size and smooth motion help robots fit in tight spots and do tasks very well.
Fast starts and stops
Exact speed control
Quiet and low vibration
High efficiency and less upkeep
Robots in factories, labs, and homes use these motors. They help robots do jobs that need quick and careful moves.
Other Uses
Coreless motors are used in more places as tech grows. You can find them in:
Wearable electronics and smart devices
Electric and self-driving cars (for seats, windows, and air systems)
Aerospace and military gear
Consumer electronics like cameras and game controllers
Makers now add sensors and smart controls to these motors. This makes them even more useful. People want smaller and more efficient products, so these motors are used more.
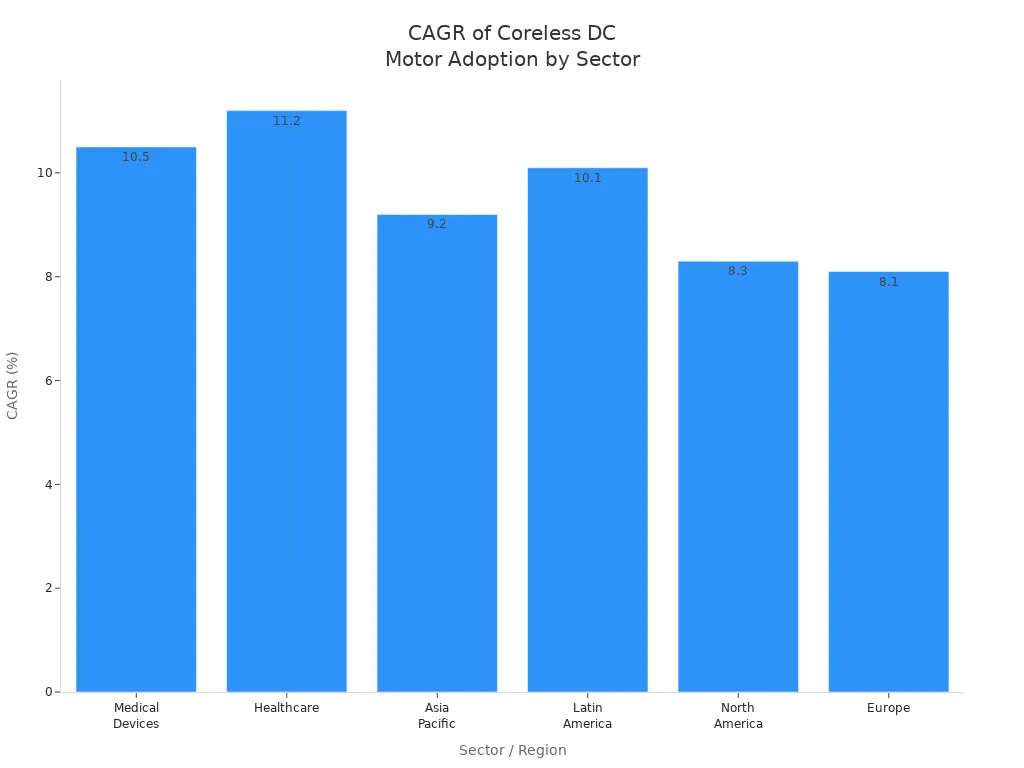
You can see big growth in healthcare, cars, and factory machines. More people want small and energy-saving solutions.
Coreless DC motors have a rotor with no iron core. This makes them work very well and move smoothly. They are also very exact. You can find these motors in robots, medical tools, and electronics. They are used when small size and accuracy are important.
Aspect | Coreless DC Motors Benefit |
|---|---|
Weight & Size | Small and lightweight |
Motion | Fast, smooth, and quiet |
Efficiency | Uses less energy, stays cooler |
Applications | Robotics, medical, aerospace, electronics |
These motors speed up quickly and make little noise.
They are best for projects that need fast and exact moves.
Think about using coreless DC motors if you want your project to work well and save energy.
FAQ
What makes a coreless DC motor different from a regular DC motor?
A coreless DC motor does not have an iron core in its rotor. This makes the motor much lighter and lets it spin faster. It moves more smoothly and does not get as hot as regular motors.
Can you use a coreless DC motor for heavy-duty tasks?
Coreless DC motors are not good for heavy work. They are best for small and light things. These motors do not make as much torque as regular DC motors.
How do you keep a coreless DC motor from overheating?
To stop overheating, do not use the motor too hard. Make sure you do not go over the motor’s limits. You can add heat sinks or fans to help cool it down. Always follow what the maker says for safe use.
Where will you find coreless DC motors in daily life?
You can find coreless DC motors in things like electric toothbrushes, drones, medical pumps, and smartwatches. These motors help your devices work quietly and use less energy.
Do coreless DC motors need a lot of maintenance?
Coreless DC motors do not need much care. Brushless types last longer and need even less work. If you have a brushed type, check the brushes sometimes and keep the motor clean.
See Also
Understanding The Vibration Generation Of 3 Volt DC Motors
Reasons To Invest In Mini Brushless Motors For Accuracy
A Comparison Between Brushed And Brushless 3V Motors
Main Distinctions Between Vibro And Conventional Motors Explained
Get Custom Micro DC Motors from
INEED Motors!
Leading Brand in Vibration Motor Manufacturing Industry
