What Is a Geared Electric Motor and How Does It Work
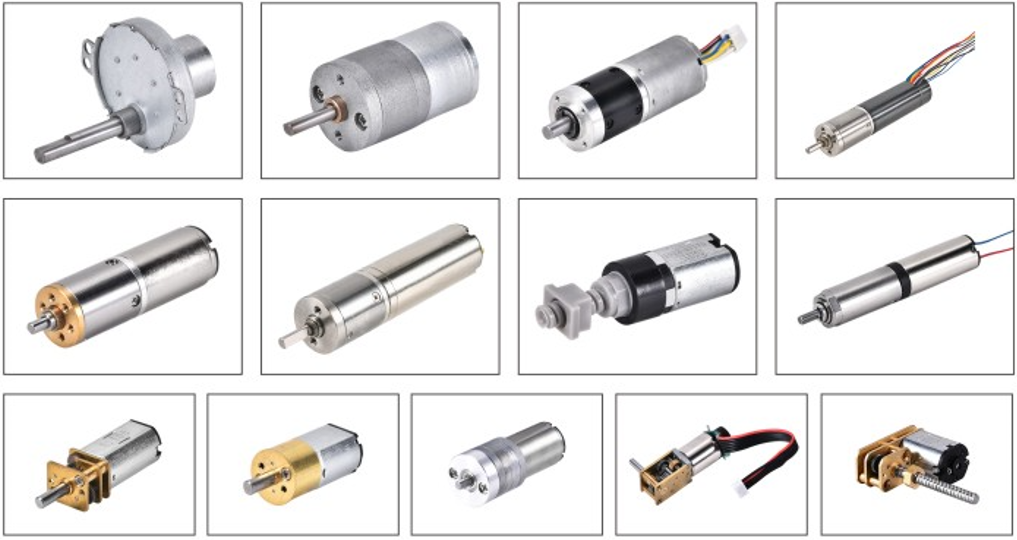

A geared electric motor is also called a gear motor. It puts an electric motor and a gearhead together in one small unit. Gear motors are used everywhere. They help give more torque and lower speed. This makes movement smooth and strong. Gear motors are important in machines that need careful motion. The market for geared electric motors is growing quickly.
Year | Market Size (USD Billion) | CAGR (%) |
|---|---|---|
2022 | 27.4 | N/A |
2030 | 57.2 | 9.52 |
You can see gear motors in many things. They are in home gadgets and factory machines.
Key Takeaways
A geared electric motor has a motor and a gearbox. It gives strong torque at low speed. This helps machines work smoothly and with power.
The main parts are the electric motor, gearbox, output shaft, and control system. These parts work together to control speed and torque well.
Gearboxes make speed lower and torque higher by using different gears. This helps machines lift heavy things and move with care.
There are different types of gear motors like AC, DC, planetary, and worm gear motors. Each type is good for certain jobs and places.
Gear motors save space and help machines work better. They are used in factories, homes, cars, and robots. This makes machines stronger and more dependable.
Geared Motor Components
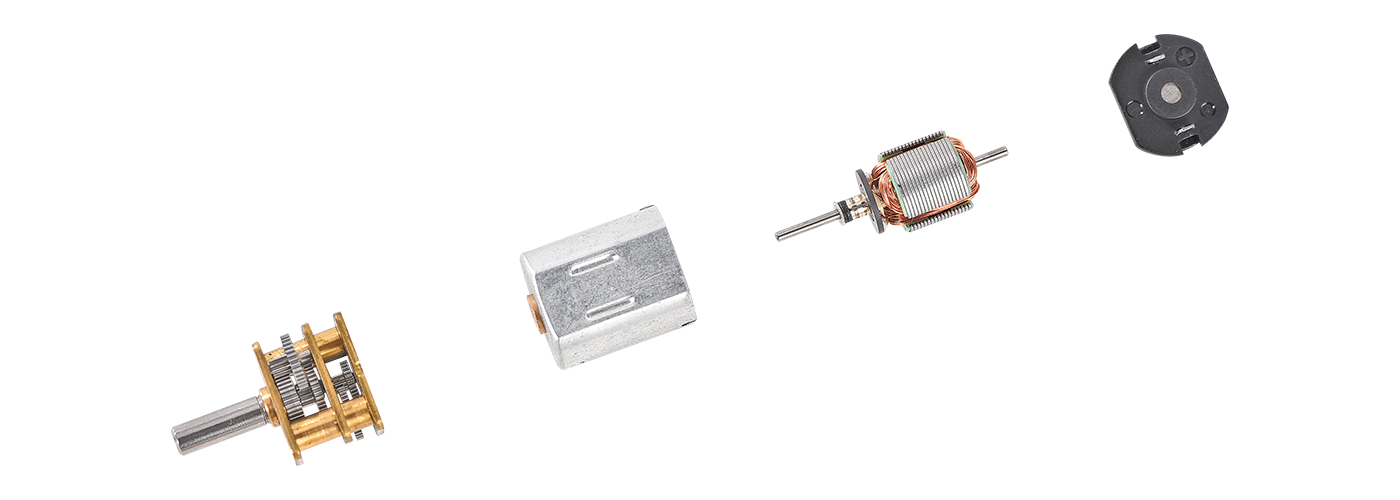
A gear motor has many important parts in one small unit. Each part helps the gear motor and gear reducer work well. The electric motor and gearhead are put together to save space and work better. Here are the main parts:
Component | Function |
|---|---|
Electric Motor | Converts electrical energy into mechanical energy; serves as the power source. |
Gearbox | Modifies speed and torque of the output shaft through gear reduction mechanisms. |
Output Shaft | Delivers mechanical power to the application (e.g., conveyor, mixer, or robot arm). |
Control System | Regulates speed and torque output for precise operation and safety. |
Electric Motor
The electric motor is the main part of every gear motor. It changes electrical energy into movement. The electric motor gives power to the whole system. In gear motors and gear reducers, the electric motor works with the gearbox to give the right force and speed. Sometimes, electric motors get too hot, bearings break, or insulation fails. Checking the motor and keeping it cool can stop these problems.
Gearhead

The gearhead, also called the gearbox or gear reducer, is joined to the electric motor. Its job is to slow down speed and make torque stronger. The gearbox uses different gears like spur, planetary, or helical gears. Spur gears have straight teeth and run quietly. Planetary gearboxes give more torque and last longer. Putting the gearhead and motor together makes the gear motor simpler and saves space. This design also lowers the chance of gears wearing out or making noise.
Tip: Integrated gear motors are shorter and fit in small spaces better than separate motor and gearhead setups.
Output Shaft
The output shaft is the part that sends power to your machine. It connects to things like a conveyor, mixer, or robot arm. The output shaft gets the changed speed and stronger torque from the gearbox. You should check the output shaft often for wear, bad alignment, or strange sounds. Oiling and checking the alignment helps the output shaft and gear motor last longer.
Control System
The control system tells the gear motor how to work. It controls speed and torque to fit your needs. Most control systems use sensors to check the motor’s speed. They compare this speed to what you want and change the voltage or frequency to keep it steady. For example, a speed sensor and comparator find any difference between real and wanted speed. The drive circuit changes the motor’s voltage with pulse-width modulation (PWM) to keep speed and torque steady, even if the load changes. This is called motor control. Checking the control system, like looking at wires and cleaning sensors, keeps it working well.
Note: Good care, like oiling and checking parts, stops common problems in gear motors and gear reducers. Always follow the maker’s rules for when to do service.
Gear motors and gear reducers put these parts together in one strong unit. This makes gear motors easy to set up, work better, and have fewer alignment issues. You get a small solution that gives high torque and steady speed for many uses.
How Geared Electric Motors Work
Understanding how geared electric motors work helps you see why they are so useful in machines. The working principle of these motors combines an electric motor with a gearbox. This combination lets you get high torque and precise control over speed. Let’s break down the process step by step.
Motor and Gearhead Interaction
When you turn on a gear motor, electrical energy flows into the motor. The motor converts this electrical energy to mechanical energy. Here is how the process works:
Electrical current moves through the stator coils inside the motor. This creates a magnetic field.
The magnetic field interacts with the rotor’s magnetic field. This interaction produces electromagnetic force.
The electromagnetic force applies torque to the rotor. The rotor starts to spin.
The speed of the rotor depends on the current and the switching of the magnetic field.
The spinning rotor sends mechanical energy through the motor shaft.
The motor shaft connects directly to the gearbox. The gearbox is the gearhead in the gear motor.
Inside the gearbox, gears with teeth mesh together. This gear reduction system changes the speed and torque.
The output shaft of the gearbox delivers the final mechanical motion. You get higher torque and lower speed at the output.
The integration of the motor and gearhead in gear motors and gear reducers gives you a compact solution. You get both high torque and precise control in one unit.
Speed Reduction
The gearbox in a gear motor plays a key role in speed reduction. The working principle of the gearbox is simple. It uses gears of different sizes to change the speed from the motor to the output shaft. When the motor spins fast, the gearbox slows down the output speed. This is called gear reduction.
A gear ratio tells you how much the gearbox reduces speed. For example, a 10:1 gear ratio means the output shaft turns once for every ten turns of the motor shaft.
Gear motors and gear reducers use gear ratios like 5:1, 10:1, or even 50:1. Higher gear ratios mean more speed reduction.
Speed reduction lets you match the output speed to your application. You can use gear motors for tasks that need slow, steady movement.
Gear Ratio | Motor Speed (RPM) | Output Speed (RPM) | Speed Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|
5:1 | 1000 | 200 | 5x slower |
10:1 | 1000 | 100 | 10x slower |
50:1 | 1000 | 20 | 50x slower |
Speed reduction in gear motors helps you get precise control over machines. You can move heavy loads slowly and safely.
Torque Increase
One of the biggest benefits of gear motors and gear reducers is torque increase. Torque is the force that makes things turn. When you use a gearbox, you trade speed for torque. The gear reduction system acts as a torque multiplier.
If your motor produces 2 Nm of torque and you use a 10:1 gear ratio, the output shaft can deliver 20 Nm of torque.
High torque is important for machines that need to lift, push, or pull heavy objects.
Gear motors let you use a small motor to get big torque at the output. This saves space and improves performance.
The gearbox multiplies torque while reducing speed. This is why gear motors work so well in applications that need both high torque and precise control. You can choose different gear ratios to match your needs. Higher gear ratios give you more torque but less speed. Lower gear ratios give you more speed but less torque.
⚡ Proper gear ratio selection improves motor performance, efficiency, and durability. It also reduces wear and noise in your system.
Keep in mind that every gear engagement in the gearbox causes some efficiency loss. Friction in the gears and bearings turns some power into heat. For example, a gearbox with a 6.3:1 ratio can be about 87% efficient. Very high gear ratios can drop efficiency below 50%. Good lubrication and regular maintenance help keep your gear motors running smoothly.
Types of Gear Motors
Gear motors come in different types. Each type works best for certain jobs. You should pick a gear motor by how it works and where you need it.
AC Gear Motors
AC gear motors run on alternating current. Most have induction motors inside. They do not use brushes, so they last longer. These motors need less care. AC gear motors give steady torque and work well for heavy jobs. You can find them in fans, pumps, and conveyor belts. Factories and big machines often use AC gear motors.
Aspect | AC Gear Motors | DC Gear Motors |
|---|---|---|
Construction | Use AC induction motors; no brushes | Brushed types have brushes; brushless use magnets |
Operation | Stable torque; less maintenance | Precise speed and torque control |
Speed & Torque Control | Less precise speed control | Superior control for precision |
Size & Weight | Bulkier and heavier | More compact and lighter |
Maintenance & Durability | Longer life; less maintenance | Brushed need brush replacement |
Efficiency | Best for heavy loads | Efficient at low speed/load |
AC gear motors are great when you need a strong motor that runs a long time.
DC Gear Motors
DC gear motors use direct current for power. You can control their speed and torque very well. Brushed dc gearmotors have brushes and a commutator. You must change the brushes sometimes. Brushless dc gearmotors use magnets and electronics. They last longer and need less care. You see dc gearmotors in robots, small machines, and toys. They are good when you need to change speed or direction a lot.
A small dc gear motor can run at about 90 volts DC. It gives good power and does not get too hot. These motors are efficient, usually between 70% and 90%. DC gearmotors are good for jobs that need careful speed control.
Planetary Gear Motors
Planetary gear motors have a special gearbox. The gears spin around a center gear, like planets. This design gives high torque and good efficiency. The motor is small and fits in tight spaces. Planetary gear motors work in cars, robots, and machines that need strong power in a small size.
Feature / Application Aspect | Planetary Gear Motors | Worm Gear Motors |
|---|---|---|
Common Industries | Automotive, robotics, machinery | Hoisting, elevators, quiet places |
Key Advantages | High torque, efficiency, compact | High torque at low speed, self-locking |
Typical Use Cases | Strong acceleration, precision | Lifting, noise-sensitive jobs |
Special Properties | Long life, good load sharing | Prevents back-driving, safe lifting |
Planetary gear motors can be over 95% efficient. You get more power and waste less energy.
Worm Gear Motors
Worm gear motors use a worm and a wheel in the gearbox. The worm looks like a screw and turns the wheel. This setup gives high torque at low speed. Worm gear motors are quiet and can stop themselves from turning backward. You see them in elevators, lifts, and places that need quiet and safe movement.
Worm gear motors are not as efficient as planetary gear motors. Their efficiency is between 30% and 60%. The sliding inside the gearbox makes heat and wastes some energy. Still, you get a small motor that can hold heavy loads safely.
Tip: Use worm gear motors if you need to stop loads from moving backward, like in hoists or lifts.
Gear Motor Technology Benefits
High Torque Output
Gear motor technology gives you high torque output. This means machines can lift heavy things more easily. Some gear motors, like the 28mm DC planetary gear motor, give up to 2.0 Nm of torque in a small size. Planetary gearboxes let many gear teeth work together at once. This design makes the torque steady and strong. Gear motor technology is good for jobs that need lots of torque and steady work. High torque output is needed in robotics and automation. These jobs need both power and careful control.
Controlled Speed
Gear motor technology lets you control speed. You can pick the speed you want for your machine. This helps you move things exactly how you want. In factories, controlled speed helps make products very accurately. Variable speed drives let you change the speed to fit your needs. You can make the gear motor go faster or slower without losing torque. Controlled speed keeps machines safe and stops them from wearing out fast. You get better results and your motor lasts longer.
Tip: Using controlled speed in gear motors helps you waste less and make better products in factories.
Compact Design
Gear motor technology has a compact design. This saves space in your machines. Small gear motors fit in tight places, like robot arms or small tools. Some motors, like the HyperFlux, give three to four times more torque than other motors the same size. You can add more moving parts or make machines lighter. Compact gear motors can take the place of big hydraulic parts. This makes your system easier to take care of. You get strong power in a small size.
Compact gear motor technology helps with:
High torque in small spaces
Light and quick designs
Easy use in crowded spots
Efficiency
Gear motor technology makes machines more efficient. New gear motors use less energy and work better. Some gear motors can use up to 30% less energy and be 50% more efficient than old ones. Good efficiency means your machines cost less to run. You also help the planet by using less power. Taking care of your gear motor, like checking oil and cleaning, keeps it working well. High efficiency and strong power make gear motor technology a smart pick for many jobs.
Feature | Regular Gearmotor | Advanced Gear Motor Technology |
|---|---|---|
Energy Use Reduction | None | Up to 30% |
Efficiency Boost | None | 50% better |
Cost to Operate | Higher | Lower |
Gearbox Efficiency | Low | High |
Note: Using gear motor technology with high efficiency helps you save money and get the best results from your motor.
Geared Motor Applications
Geared electric motors are used in many real-life jobs. You find them where strong torque and steady speed are needed. These motors help machines work better, especially when high torque is important. Let’s see some ways they are used in different areas.
Industrial Machinery
Factories use geared motors in machines like conveyors and mixers. These motors help move heavy things and keep work going. In automation, geared motors let you control speed and direction well. This makes machines work better and saves energy. You can count on these motors for hard work in factories and warehouses.
Some ways geared motors are used in industry:
Conveyor belts move products
Mixers blend materials
Assembly lines put things together
Lifting systems raise heavy items
Tip: Check the torque and speed before picking a geared motor for your machines.
Home Appliances
You use geared motors in many home devices. Washing machines, drills, and food processors need these motors. They give the right speed and torque for each job. In smart homes, geared motors open blinds or move recliners. This makes your home more comfortable and easy to use.
Some ways geared motors are used at home:
Washing machines spin and mix clothes
Electric screwdrivers turn screws
Automatic blinds open and close
Automotive
Cars use geared electric motors for seats, windows, and sunroofs. These motors must give strong torque and work quietly. You get smooth and safe movement in your car. The table below shows how these motors are used in cars:
Feature Category | Details |
|---|---|
Applications | Seat adjustment, automobiles, vehicles, window systems |
Motor Types | DC, brushless DC, AC, permanent magnet, synchronous, brushed |
Gear Types | Planetary, worm, gear train, helical, spur, bevel |
Torque Ranges | 0.2 - 50 Nm (various ranges) |
Mounting Options | Flange-mounted, shaft-mounted |
Performance | High torque, low noise, high efficiency, precision, suitable for heavy loads |
You get motors that work well and stay quiet in your car’s systems.
Robotics
Robots need geared motors for moving and control. In robot arms, these motors give the right torque and accuracy for each joint. The table below shows how each part helps the robot arm move:
Component | Role in Robotic Arm Movement |
|---|---|
Actuator (Geared Electric Motor) | Changes electrical energy to movement for joints. |
Reduction Gear | Makes the motor stronger by lowering speed and raising torque. |
Encoder | Tells the robot where the motor shaft is for control. |
Transmission | Sends power from the motor to the joints. |
Servo Motor | Gives high accuracy and speed for robot arm movement. |
You use geared motors in robots to get good performance and smooth moves. These motors help robots lift, move, and place things carefully.
Note: When picking a geared motor for robots, think about torque, efficiency, and how well it works for your needs.
You now know that geared electric motors have an electric motor and a gearbox together. This helps them give strong torque at slow speeds. These motors use many gear types for different jobs. You can find them in robots and home appliances. Gear motors help machines work better and use less energy. They also help machines last longer.
Gear motors are important in today’s industry and in your life. They make machines stronger and more dependable.
For more information, look at:
Getting The Most From Your Electric Motors (free booklet)
Mechanical Design of Electric Motors by Wei Tong
YouTube channels for learning, like BigBadTech and MunroLive
FAQ
What is the difference between a gear motor and a regular motor?
A gear motor has a gearbox attached to the motor. This setup gives you more torque and lower speed. A regular motor does not have a gearbox, so it spins faster but with less force.
How do you choose the right gear motor for your project?
You should check the torque and speed your machine needs. Look at the size and power of the gear motor. Make sure it fits your space and matches your voltage. Ask the supplier if you need help.
How long does a gear motor last?
Most gear motors last several years if you take care of them. You should keep them clean, check for noise, and add oil when needed. Good maintenance helps your gear motor work longer.
What should you do if your gear motor makes noise?
Noise can mean a problem with gears or bearings. You should stop the motor and check for loose parts or low oil. If you see damage, replace the bad parts. Regular checks help prevent noise.
See Also
Selecting The Best Planetary Gear Motor For Precision Screwdrivers
How To Pick Battery Powered Motors For Maximum Efficiency
Maintaining Electric Vibration Motors To Boost Longevity And Output
A Guide To Interpreting And Understanding Motor Diagrams Easily
Exploring ERM Vibration Motor Diagrams: Components, Types, And Uses
Get Custom Micro DC Motors from
INEED Motors!
Leading Brand in Vibration Motor Manufacturing Industry
