How to Design a Drive Circuit for LRA Vibration Motors
Do you think you can drive the LRA motor as easily as you drive other vibration motors? That's wrong. The secret to its precise and sensitive touch lies in a narrow resonant frequency range - you need to precisely reach this frequency, rather than relying on brute force to drive it.
This guide will decrypt this crucial engineering challenge: design a driving circuit that not only provides power but also actively tracks and locks onto this resonant point. If designed properly, you will achieve unprecedented high efficiency and realistic tactile sensations; conversely, if the design is not appropriate, you will face weak feedback and energy waste problems.
Are you ready to transition from theoretical knowledge to practical application? We will elaborate on the steps to achieve resonance, select the appropriate driving chip, and implement control to ensure stable and reliable performance. Understand how a properly tuned circuit can enhance your user experience and explore how collaborating with experts like INEED Motors can simplify the entire process from design to large-scale production.
Key Takeaways
Design a drive circuit that matches the resonant frequency of the LRA motor for optimal performance and energy efficiency.
Select a suitable driver IC to control the LRA, ensuring it meets power efficiency and compatibility requirements.
Use proper layout techniques and damping materials to enhance vibration strength and reduce unwanted noise in your device.
Regularly prototype and test your circuit to catch issues early and ensure reliable haptic feedback.
Choose INEED's LRA motors for their low power consumption and strong performance, ideal for wearable technology.
LRA Vibration Motor Basics
What Is a Linear Resonant Actuator
You encounter many types of vibration motors in electronic devices, but the linear resonant actuator stands out for its precision and efficiency. A linear resonant actuator is a type of vibration motor that uses a voice coil and a moving mass. The coil receives an alternating current (AC) signal, which causes the mass to move back and forth. This movement creates vibration at a specific frequency. You see linear resonant actuators in devices that need fast and accurate haptic feedback, such as smartphones, game controllers, and wearable technology.
Tip: The INEED LRA Electrical Motor LRA2024A-1088F is a great example of a linear resonant actuator. It delivers strong vibration and quiet operation, making it ideal for haptic feedback in advanced electronics.
Here is a table that shows how a linear resonant actuator compares to an eccentric rotating mass motor:
Feature | Linear Resonant Actuator (LRA) | Eccentric Rotating Mass (ERM) Motor |
|---|---|---|
Operating Principle | Uses AC voltage to drive a voice coil with a moving mass | Uses a DC motor with a counterweight |
Vibration Generation | Generates vibrations at its resonant frequency | Creates vibrations through centripetal force |
Control | Precise control of vibration frequency and amplitude | Vibration characteristics depend on rotational speed |
How LRA Vibration Motors Work

You need to understand how LRAs work to design an effective drive circuit. The vibration motor operates at its resonant frequency, which is a narrow range where the vibration amplitude reaches its peak. If you drive the motor outside this frequency, the vibration drops sharply or stops. This is why you must use an AC signal that matches the resonant frequency of the linear resonant actuator.
You get the best haptic feedback when the vibration motor runs at its resonant frequency. The INEED Linear Vibration Motors, including the LRA2024A-1088F, are designed to maximize vibration and energy efficiency. These motors use a voice coil and spring system to create vibration along the z-axis. You can control the frequency and amplitude with high precision, which is essential for applications like wearable devices and gaming systems.
You should select a driver circuit that can track and adjust to the resonant frequency.
You achieve strong, reliable haptic feedback by matching the drive signal to the motor’s resonance.
The unique design of LRAs makes them perfect for applications where you want quick response, stable vibration, and long-lasting performance.
Essential Components for LRA Drive Circuits
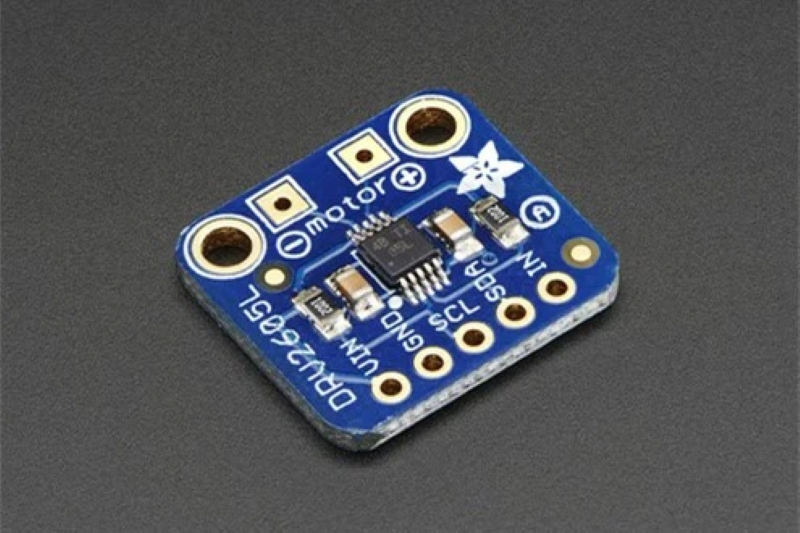
Designing a reliable drive circuit for an lra requires you to understand the main components that make the system work. Each part plays a unique role in producing precise haptic feedback. You need to focus on the voice coil, the driver IC, and the power supply. These elements work together to deliver strong and efficient vibration in your device.
Voice Coil and Resonance
The voice coil sits at the heart of every lra. When you apply an AC voltage, the coil generates oscillations in a mass attached to a spring. This movement creates the vibration you feel. The system works best when you drive the motor at its resonant frequency. At this point, the vibration reaches its maximum strength, and the motor uses less energy. If you move away from this frequency, the vibration weakens, and the motor draws more power.
You can see this principle in INEED’s lra vibration motor lineup. For example, the LRA2024A-1088F uses a voice coil and spring system to deliver strong, consistent vibration. This design ensures you get reliable haptic feedback with low power consumption. The motor’s ability to operate efficiently at resonance makes it ideal for wearable devices and other battery-powered products.
Note: Always match your drive signal to the lra’s resonant frequency. This step ensures you get the best vibration performance and extend battery life.
Driver IC Selection
You need a dedicated driver IC to control the lra. The driver IC generates the precise AC signals that keep the motor operating at its resonant frequency. Choosing the right IC affects the quality of your haptic feedback and the efficiency of your system. Popular options include the TI DRV2605 and the awinic AW86223. These chips offer advanced features for controlling vibration intensity and frequency.
When you select a driver IC, consider the following criteria:
Evaluation Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
Power Efficiency | Minimizes energy use, important for battery-powered devices. |
Size & Form Factor | Small chips fit easily into compact devices like wearables. |
Driving Capabilities | Supports different vibration strengths and frequencies. |
Thermal Management | Prevents overheating during long use. |
Compatibility & Integration | Works well with your existing hardware and software. |
Reliability & Longevity | Stands up to wear and environmental stress. |
Cost & Supply Chain | Offers good pricing and stable availability. |
Vendor Support & Documentation | Provides technical help and clear datasheets. |
INEED’s lra motors, such as the LRA2024A-1088F, work seamlessly with these driver ICs. This compatibility gives you flexibility in your design and helps you achieve the haptic effects you want.
The lra drive circuit may cost more than basic ERM solutions because of its complexity.
However, it remains more affordable than high-end haptic systems like VCM or Piezo.
Power Supply Considerations
The power supply you choose must meet the voltage and current needs of your lra vibration motor. Supplying the correct power ensures stable operation and protects the motor from damage. Most lra motors for wearables run at low voltages and draw little current. This feature helps you save battery life and keep your device running longer.
Here are typical power requirements for lra motors in wearable devices:
Specification | Value |
|---|---|
Rated Voltage (Vac RMS) | 1.8 |
Operating Voltage (Vac RMS) | 0.1~1.9 |
Rated Current MAX (mA) | 80 |
Typical Current (mA) | 58 |
INEED’s lra motors stand out for their low power consumption and strong vibration output. For example, the LRA2024A-1088F delivers powerful haptic feedback while using less energy than many other vibration motor types. This efficiency makes it a top choice for smartwatches, fitness bands, and other portable electronics.
Attribute | Linear Resonant Actuators (LRAs) | Eccentric Rotating Mass (ERM) |
|---|---|---|
Power Consumption | Low (typically 2V) | Higher |
Tip: Always check your lra motor’s datasheet for the recommended voltage and current. Using the right power supply helps you avoid performance issues and extends the life of your haptic system.
By understanding the roles of the voice coil, driver IC, and power supply, you can design a drive circuit that brings out the best in your lra vibration motor. This approach ensures you deliver precise, efficient, and reliable haptic feedback in your next device.
Drive Circuit Design Steps
Designing a vibration motor circuit for an LRA vibration motor requires careful planning and attention to detail. You need to follow a step-by-step approach to achieve reliable haptic feedback and long-lasting performance. This section guides you through the essential steps, from schematic creation to resonance tuning and practical implementation.
Schematic and Layout
You start by drawing the schematic for your vibration motor circuit. Place the LRA vibration motor, driver IC, and power supply in the diagram. Make sure you connect each component according to the datasheet instructions. You should keep signal paths short and direct to reduce unwanted noise.
Layout plays a big role in the performance of your haptic system. You want to minimize audible buzzing and maximize vibration strength. The table below shows important layout considerations:
Consideration | Description |
|---|---|
Operating Frequency Range | Operating within the specified frequency range minimizes audible buzzing. |
Damping Materials | Using proper damping materials can further reduce sound emissions. |
Mounting and Integration | Securely attach the LRA actuator and ensure proper alignment to prevent issues. |
You improve the reliability of your vibration motor circuit by using damping materials and mounting the motor securely. You also need to align the actuator properly to avoid mechanical problems. INEED’s LRA motors, such as those used in wearable devices, benefit from these layout practices. You get stronger haptic feedback and quieter operation.
Resonance Tuning
You must tune the resonance frequency to get the best vibration from your motor. The LRA vibration motor works best at its resonant frequency, so your circuit needs to keep the motor at this point. You use driver circuits that monitor resonance and adjust the signal automatically. Back-EMF monitoring helps you maintain the motor at the optimal frequency.
You can use control methods like pulse-width modulation, overdrive, and braking signals to fine-tune vibration strength and timing. These techniques let you match the motor’s vibration to your device’s needs. You test the resonance frequency with a signal generator to make sure the motor and circuit work together for maximum haptic performance.
Tip: Always prototype and test your vibration motor circuit before finalizing the design. You catch problems early and ensure the motor delivers the haptic feedback you expect.
Implementation Tips
You improve the reliability and lifespan of your vibration motor circuit by following practical steps. Use driver chips to control the LRA vibration motor and ensure efficient vibrations. Test the resonance frequency during development to align the motor’s performance with your device’s design.
Regular troubleshooting keeps your haptic system running smoothly. You can use infrared thermography to detect overheating components. Monitor voltage and current levels with a multimeter to prevent burnout. Lubricate moving parts as recommended to reduce friction and wear. Reduce the motor’s workload if you notice overheating, and make sure the device has proper ventilation. Clean and inspect the motor regularly to prevent dust and moisture damage.
Prototype and test your vibration motor circuit before mass production.
Use driver chips for precise haptic control.
Monitor and maintain your motor to extend its lifespan.
INEED’s solutions for wearable devices show how these steps lead to reliable haptic feedback and long-lasting vibration performance. You get a better user experience and fewer maintenance issues when you follow these guidelines.
INEED Linear Resonant Actuator Solutions
Product Features and Benefits
You can rely on INEED’s LRA Electrical Motor LRA2024A-1088F and Linear Vibration Motors for advanced haptic applications. These motors stand out because they deliver precise tactile feedback and strong, consistent vibrations. The LRA2024A-1088F operates at a resonant frequency of 65Hz, which feels more comfortable for the human body than the higher frequencies used by many competitors. You get a wide frequency range from 30Hz to 500Hz, so your device can create a variety of tactile sensations.
Here is a table that summarizes the key features of the LRA2024A-1088F:
Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Ultra-comfortable resonant frequency | Operates at 65Hz for a natural tactile experience |
Ultra-wideband capability | Delivers strong vibrations from 30Hz to 500Hz |
Precision powers immersion | Fast response times under 20ms for immersive haptic feedback |
Haptic feedback | Simulates real-world interactions through tactile signals |
Exciting force generation | Produces strong driving force for enhanced tactile effects |
You also benefit from high energy efficiency. LRA vibration motors use resonant linear motion, which saves more energy than traditional ERM vibration motors that rely on rotational movement. INEED’s motors meet strict quality standards, including RoHS, ISO9001, ISO14001, and ISO045001 certifications. These standards ensure your devices remain safe and reliable.
Application in Wearable Devices
You see the advantages of INEED’s lra motors in wearable technology. These vibration motors fit easily into smartwatches and health monitors because of their compact size and light weight. You get accurate and steady tactile feedback, which improves the user’s interaction with the device. The motors respond quickly, so you feel every alert or notification right away.
Here is a table showing the benefits for wearable devices:
Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
Energy Efficiency | Quick response and low power use for longer battery life |
Compact Size | Small and light, perfect for wearable devices |
Accurate Haptic Feedback | Delivers steady and precise tactile sensations |
You improve the tactile experience for users by choosing lra vibration motors. These motors have become popular in high-end smartwatches and health monitoring systems. The demand for precise tactile feedback in consumer electronics and healthcare devices continues to grow. You can trust INEED’s solutions to deliver reliable haptic performance in your next wearable project.
You design an effective vibration motor drive circuit by following these steps:
Select the target frequency for your application.
Generate an AC signal at that frequency.
Adjust the amplitude for the desired vibration strength.
Monitor and fine-tune the actuator’s response.
Proper component selection and resonance tuning ensure reliable haptic feedback. INEED provides technical resources and expert support for engineers:
Resource | Description |
|---|---|
C0825 Coin LRA Vibration Motor | Expertise in risk mitigation and customization. |
LRA Electrical Motor LRA2024A-1088F | Custom solutions and driver compatibility. |
Vibration Motor | Tailored haptic feedback for unique applications. |
Explore INEED’s website for more guidance and solutions.
FAQ
What is the main advantage of using an LRA vibration motor?
You get precise haptic feedback with fast response times. LRAs use less power than traditional motors. You can customize vibration frequency and amplitude for your application.
How do you select the right driver IC for an LRA motor?
You should check the motor’s datasheet for recommended ICs. Look for chips like TI DRV2605 or awinic AW86223. These support frequency control and efficient power use.
Can you use an LRA motor in wearable devices?
Yes, you can. LRAs fit easily into smartwatches and fitness bands. You get strong vibration and low power consumption, which helps extend battery life.
What should you do if the vibration feels weak?
Tip: Test the drive signal frequency. Make sure it matches the motor’s resonant frequency. Adjust the driver IC settings for stronger vibration.
See Also
Enhancing LRA Motors for Effective Vibrating Object Applications
Key Role of LRA Vibration Motors in Haptic Feedback Technology
Maximizing Efficiency by Tuning LRA Vibration Motors' Resonance Frequency
Exploring ERM Vibration Motors: Components, Types, and Uses
Understanding Frequency and Vibration Effects on LRA Motor Performance
Get Custom Micro DC Motors from
INEED Motors!
Leading Brand in Vibration Motor Manufacturing Industry
