3 Key Differences in AC Motor vs DC Motor
When you compare ac motor vs dc motor, three big differences stand out: the type of electric power they use, how you control their speed, and what it takes to keep them running. AC motors use alternating current, while dc motors use direct current. You will also notice differences in efficiency, speed control, and maintenance. Check out this quick table to see how these electric motors stack up:
Aspect | AC Motors | DC Motors |
|---|---|---|
Power Source | Alternating current (changes direction) | Direct current (constant voltage) |
Speed & Efficiency | 2-pole = 3000 rpm, 4-pole = 1500 rpm | 88-92% efficiency, wide speed range |
Maintenance | Low, no brushes | Needs brush checks every 3 months |
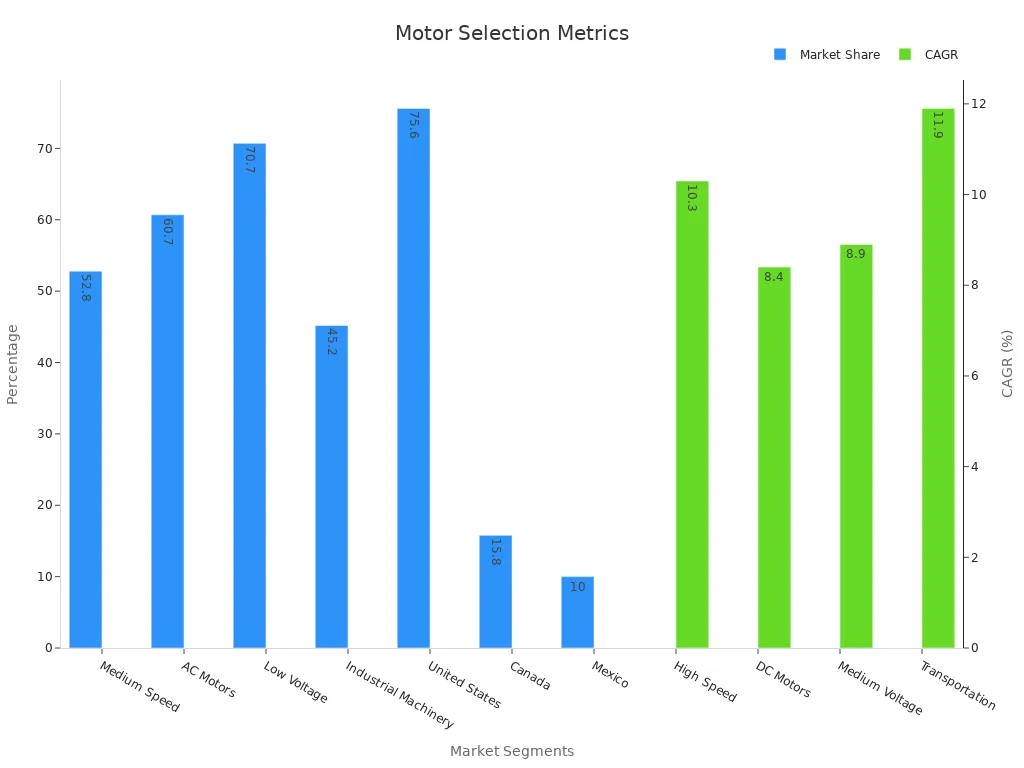
Choosing the right electric motor matters. In the United States, ac motors hold over 60% of the market because of their reliability and efficiency, but dc motors keep growing fast for electric vehicles and robotics.
Key Takeaways
AC motors use alternating current, making them ideal for steady power and long-distance electricity delivery in homes and industries.
DC motors run on direct current, offering easy and smooth speed control, perfect for battery-powered devices and electric vehicles.
AC motors need less maintenance because they have no brushes, which lowers long-term costs and boosts reliability.
DC motors require regular brush checks but provide strong torque and flexible speed, great for robotics and portable tools.
Choose AC motors for simple, low-upkeep use and DC motors when you need quick speed changes and high energy efficiency.
1. Power Source: AC Motor vs DC Motor
AC Motors: Alternating Current
When you look at ac motors, you see that they run on alternating current. This means the electric power changes direction many times each second. Most homes and businesses use this type of power. You can plug in an ac motor almost anywhere because the electric grid supplies alternating current. This makes ac motors a popular choice for things like fans, washing machines, and air conditioners.
Alternating current lets you send electric power over long distances without losing much energy.
You can easily change the voltage of ac power using transformers.
Most household appliances and large machines use ac motors because of this flexibility.
DC Motors: Direct Current
On the other hand, dc motors use direct current. The electric power flows in only one direction and stays steady. You often find dc motors in battery-powered devices, like remote-control cars or electric scooters. These motors get their power from batteries or special adapters that turn ac into dc.
Direct current gives a constant voltage, which helps dc motors deliver smooth and steady performance.
You usually see dc motors in electronics, toys, and electric vehicles.
Early electric systems used dc, but they could not send power far because of voltage drops.
Why Power Source Matters
The type of electric power shapes how each motor works and where you use it. Here is a quick table to help you compare:
Characteristic | AC Motors | DC Motors |
|---|---|---|
Power Source | Alternating current (changes direction) | Direct current (one-way, steady) |
Voltage Behavior | Fluctuates in a wave pattern | Stays constant |
Common Use | Home appliances, industry | Battery devices, electronics |
Distance Power Travels | Long distances with little loss | Short distances, local use |
When you compare ac motor vs dc motor, you notice that ac motors work best when you need reliability and easy access to electric power. Dc motors shine in portable or battery-powered devices where steady power is important. The power source not only affects how you connect your motor but also impacts its design, efficiency, and where you will use it.
2. Speed Control & Performance

AC Motors: Speed Control
When you use ac motors, you control speed by changing the frequency of the electric power. Most ac motors run at a fixed speed, but you can add a Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) to adjust the speed smoothly. VFDs work by converting the standard electric supply into a variable frequency and voltage. This lets you set the motor speed for your needs.
You can use Scalar (V/F) Control for simple, steady speed changes.
Vector Control gives you more precise and responsive speed control, even at low speeds.
Some advanced drives reach speed accuracy up to 0.3%, which is great for jobs that need fine control, like elevators or CNC machines.
VFDs also help with controlled acceleration, torque limiting, and braking, making ac motors flexible for many electric applications.
DC Motors: Speed Range
You get a wide speed range with dc motors. You can change the speed by adjusting the voltage or current. This makes dc motors easy to control, even without extra equipment. You often see dc motors in electric vehicles, robotics, and toys because you can make them go fast or slow with simple controls.
You can use a knob or switch to change the speed quickly.
DC motors give you smooth speed changes and steady torque.
These motors work well in battery-powered devices, where you need flexible speed and direction.
Performance Implications
Choosing between ac motor vs dc motor depends on your speed control needs. If you want precise speed and torque control, ac motors with VFDs or vector drives work best for heavy-duty electric machines. These motors also improve energy efficiency and reduce wear by allowing smooth starts and stops. In factories, ac motors help run large fans, pumps, and conveyors at a steady pace.
If you need a motor for a device that changes speed often, dc motors are a better fit. You get quick, simple speed adjustments, which is perfect for electric vehicles, robotics, or small gadgets. DC motors also shine in applications where you need steady performance at different speeds.
Tip: For constant speed and high energy efficiency, pick ac motors with advanced drives. For easy speed changes and portable electric devices, dc motors are your best choice.
3. Applications & Maintenance
AC Motors: Typical Uses
You will find ac motors in many places that need steady, reliable power. These motors work best in high-power and constant-speed jobs. You see them in pumps, compressors, and large fans. Many factories use ac motors for conveyors and HVAC systems. Water and wastewater treatment plants rely on them because they handle big loads and run for long hours. The steel and mining industries also use ac motors for their energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Here is a quick look at where ac motors shine:
Sector / Application | Why Use AC Motors? |
|---|---|
Water & Wastewater Treatment | Handles heavy loads, runs efficiently |
Steel & Mining | Delivers reliable, high-power performance |
HVAC Systems | Keeps air moving with low maintenance |
Automotive Manufacturing | Supports assembly lines with steady operation |
AC motors help you save energy and lower costs in large-scale electric systems. Their reliability makes them a top choice for industries worldwide.
DC Motors: Typical Uses
You will often choose dc motors when you need flexible speed and strong torque at low speeds. These motors work well in electric vehicles, robotics, and automation. You see dc motors in battery-powered tools, drones, and conveyor belts that need quick speed changes. Many home appliances, like air conditioners and fuel pumps, use brushless dc motors for better energy efficiency and longer life.
Check out these common uses for dc motors:
Electric vehicles: Delivers smooth acceleration and easy speed control.
Robotics: Offers precise movement and quick direction changes.
Home appliances: Runs quietly and saves energy.
Industrial automation: Provides accurate control for machines and tools.
A table below shows more details:
Application Area | Benefit of DC Motors |
|---|---|
Electric Vehicles | High torque, easy speed adjustment |
Robotics | Accurate, repeatable motion |
Home Appliances | Energy efficiency, quiet operation |
Automation | Simple control, reliable performance |
Maintenance Needs
You want your electric motor to last and work well. AC motors usually need less maintenance because they have fewer moving parts. They do not use brushes, so you avoid regular brush checks and replacements. This design boosts reliability and lowers long-term costs. AC motors also handle tough environments and keep running with little attention.
DC motors have a simpler design, but you must check and replace brushes over time. Brushless dc motors last longer and need less care, making them a smart pick for many electric devices. Still, dc motors may cost more upfront, but their cost-effectiveness improves with longer life and fewer breakdowns.
Here are some key points to remember:
AC motors: Less maintenance, more robust, lower long-term cost.
DC motors: Simple design, predictable brush replacement, higher initial cost.
Both types: Modern designs improve energy efficiency and reliability.
Tip: If you want low maintenance and high reliability, choose ac motors. For easy speed control and strong torque, dc motors are your best bet.
You can remember the three main differences: power source, speed control, and maintenance. To help you choose the right motor, check this quick guide:
Criteria | AC Motor | DC Motor |
|---|---|---|
Efficiency | Medium | High |
Control | Needs extra parts | Easy |
Cost | Lower | Higher |
Reliability | High | Medium |
Pick AC if you want simple use and low upkeep.
Pick DC if you need easy speed changes and strong power.
Think about your budget, how much control you want, and where you will use the motor.
For more details, look for guides on motor selection and decision matrices that compare features like efficiency, cost, and reliability.
FAQ
What is the main advantage of using an AC motor?
You get reliable performance and low maintenance with AC motors. They work well for most home appliances and industrial machines. You can find them almost everywhere because they use the same power as your wall outlets.
Can you use a DC motor with household electricity?
No, you cannot connect a DC motor directly to household electricity. You need a power adapter or converter to change AC to DC. Most DC motors run on batteries or special power supplies.
Which motor lasts longer, AC or DC?
AC motors usually last longer. They have fewer parts that wear out, like brushes. You spend less time and money on repairs. DC motors need regular brush checks, unless you use brushless types.
Are AC motors or DC motors more energy efficient?
DC motors often give you higher energy efficiency, especially at different speeds. You save more power in battery devices or electric vehicles. AC motors work best at constant speeds and still offer good efficiency for large machines.
See Also
Differences Between Brushed And Brushless Motors At 3 Volts
Understanding The Main Differences Between Vibro And Standard Motors
How To Choose The Best 3 Volt DC Motor For Projects
Get Custom Micro DC Motors from
INEED Motors!
Leading Brand in Vibration Motor Manufacturing Industry
